TEAMTOX research project: preventing mycotoxin contamination of wheat requires a new paradigm
Despite extensive research over the past decades and significant advances in knowledge, recommended agricultural practices are not sufficient to ensure levels of mycotoxins that are in line with regulatory limits. To date, research aimed at providing a basis for the development of mycotoxin control strategies has been conducted almost exclusively by looking at a ‘single disease agent-single disease’, an approach that has proven insufficient to achieve a comprehensive understanding of the disease. Fusarium wilt disease process and mycotoxin accumulation in crops. In fact, the mixture of species fusarium Interaction in a shared ecological niche is likely to produce mycotoxins that have their own regulation that cannot be predicted by studying individual fungal species. Obviously, interactions between species fusarium Go beyond the simple “1 + 1 is 2” theorem. A paradigm shift is needed: the approach focuses on one type of fusarium must be exceeded.
This challenge directs the TEAMTOX project which proposes to consider the Meta-fusarium s. as a single individual.
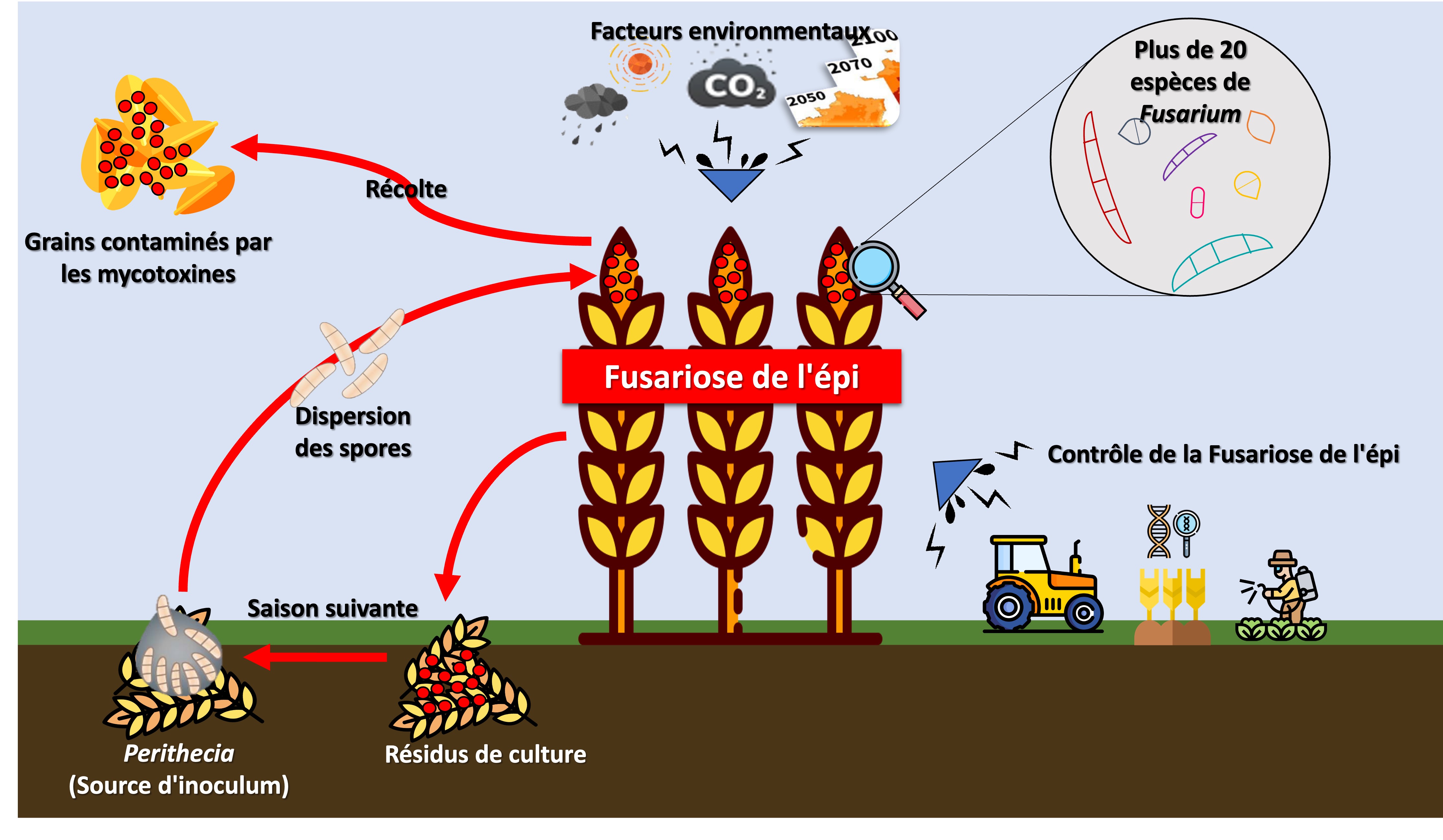
Fusarium head blight: The cycle of infection and contamination with mycotoxins is affected by many environmental and agricultural factors. (Illustration: Valentin Fiévet, PhD recruited as part of the TEAMTOX project)
Meta-Fusarium sp. : Studied 7 pathogenic fungi as one
in In this context, the goal of TEAMTOX is to decipher the regulation of the biosynthesis of mycotoxins produced by what we call ‘Meta-fusarium s.Meta-fusarium s. , which includes the main types of fusarium involved in FHB, would be considered in analyzes of ecophysiology as an individual fungus functioning as a single organism. The innovative approach underlying the TEAMTOX research project will pave the way for better strategies to control fusarium wilt and mycotoxins. It will demonstrate the need to go beyond reductionist approaches centered on a single fungal species to identify and validate the effectiveness of new alternatives to synthetic fungicides.
To validate the interest of the new paradigm guiding the TEAMTOX project and propose a methodology and data for the use of Meta-fusarium s.And Research activities are organized around four questions about the biological functioning of meta-fusarium s.
1.) What are the dynamics of Meta- formationfusarium s. and its production of secondary metabolites under abiotic stresses ? The aim is to describe the distribution kinetics of the species fusarium and profiles of mycotoxins produced by Meta-fusarium s. As well as to determine disturbances caused by various abiotic factors including temperature and redox potential in the environment.
2.) How is mycotoxin production regulated by Meta-fusarium s. When exposed to abiotic stresses? Genomic and epigenetic studies will be conducted to identify the molecular events leading to the production of mycotoxins by Meta-fusarium s.with regard to the dynamics of its formation.
3.) Does the specific endogenous genetic diversity of one of the constituent species have a significant impact on the formation and functioning of meta-fusarium s. ? Species fusarium They are known to show extreme genetic and phenotypic diversity, which is associated with a strong adaptive potential. By replacing a strain of one of the constituent species of Metafusarium s. by other genetically different strains, we will characterize the effect of stress on Meta-fusarium s. and his profile of mycotoxins.
4.) vulnerability to meta-fusarium s. For biomolecules and biocontrol agents different from those in the constituent species? metafusarium s. Can they help improve effectiveness evaluation trials? The goal is to support the added value of Meta-fusarium s. By evaluating the effects of biocontrol candidates whose biological activity has been previously demonstrated through methods in the laboratory Focus on one type. It is indeed more than likely that the efficacy of these biosynthetic solutions is strongly modulated in the cases of biosynthetic interactions.
Significant scientific progress is expected from the TEAMTOX project, which will provide new knowledge about the determinants of mycotoxin accumulation in cereal crops and the mechanisms that regulate their production. These developments will illustrate the interest in the search for meta-pathogens, a new concept that could also benefit research initiatives related to other fungal plant diseases. All data obtained in TEAMTOX will contribute to improving strategies for controlling Fusarium wilt and mycotoxin contamination as well as reducing the use of synthetic fungicides. Reducing economic losses in the grain sectors and reducing consumer exposure to toxic particles are the two ultimate goals of the project.

“Organizer. Social media geek. General communicator. Bacon scholar. Proud pop culture trailblazer.”